GA4 MIGRATION RESOURCE CENTER
Step Four: Exclusions and Filters
AT A GLANCE
Exclude unwanted referrals and filter internal traffic from data streams.
Validate all exclusions and filters with tests prior to impacting data streams.
Referral Exclusions and Filters
After creating data streams for a GA4 property, preserve data integrity and clarity by removing distracting traffic generated by automated apps, integrated tools, or internal developers.
Key Tasks
- Exclude unwanted referrals for a property, such as payment vendor traffic, automation tools, etc. whose traffic doesn’t represent true referrals of relevant user traffic
- Exclude unwanted referrals for specific events by appending the ignore_referrer parameter to individual pages or events set to “true.”
- Filter internal traffic for a property
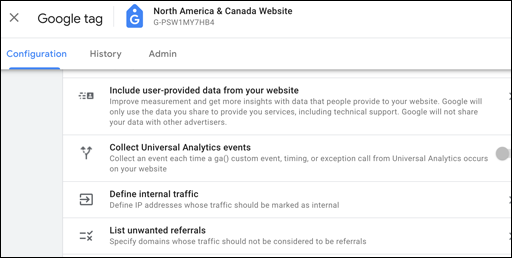 Tag Settings Dialog
Tag Settings Dialog
Overview
A legacy UA implementation likely has multiple referral exclusions or an internal filter to ensure data streams do not mix targeted visitor traffic with internal developer or utility app traffic. Exclusions and filters are critical to maintaining clean data, are simple to set up, and must be validated prior to impacting the data stream. Exclusions and filters should be tested before changing data. Ensure that adequate definition is conducted before enacting changes to a business data stream.
Exclude Unwanted Referrals (Property Level)
Often a website uses third-party domains to process payments or to provide automation apps. Traffic to your site that comes from a third-party domain displays in the referrals traffic segment. To ensure your data includes only referrals in which you’re interested, you can exclude these unwanted referrals from your data. To configure unwanted referrals, navigate to your web data stream, and select Configure tag settings > Show all. Click List unwanted referrals and select match condition(s) and domain(s). For example: “contains” “paypal”.
If you are uncertain which domains need referral exclusion, review your User Acquisition report with page_referrer (previous page URL) dimension added. By reviewing all referring sources, you can identify payment gateways, tools and apps domains that do not represent additional unique users.
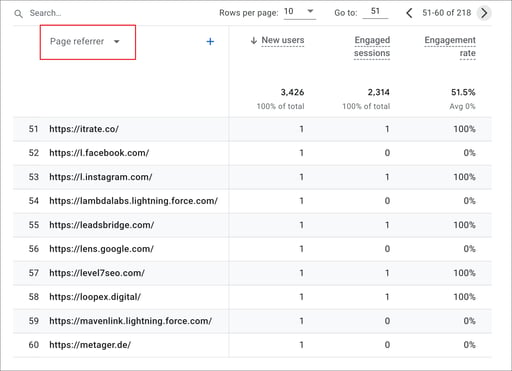 User Acquisition Report - Page Referrer
User Acquisition Report - Page Referrer
Exclude Unwanted Referrals (Event Level)
While unwanted referrals are usually set globally (e.g., filter all paypal transaction traffic), you may need to ignore referrers only in certain situations. You can append an ignore_referrer parameter to individual pages or events and set it to true. For example, to ignore a referrer on a specific page, add the parameter to the config command:
Google notes that most site owners will not need to do this. Do not append the parameter manually if unsure of the function and how it impacts data streams. The specific circumstance for such a localized exclusion is unique and should be carefully defined before implementing manual exclusions across pages.
Need help with implementation?
Uncover customer journeys and accelerate conversions with GA4’s advanced AI and data-driven attribution We can help you get there.
Exclude Internal Traffic
Since GA is most often used to track external customers and users interacting with your website, internal traffic is typically distracting when mixed with prospect and customer traffic. Filtering out internal traffic makes analytics easier to understand customer behavior.
When a GA4 property is created, a filter for internal traffic is also created. The filter defines any traffic with the parameter traffic_type with a value of internal. To trigger the filter, users need only create a rule to identify which traffic matches that parameter value.
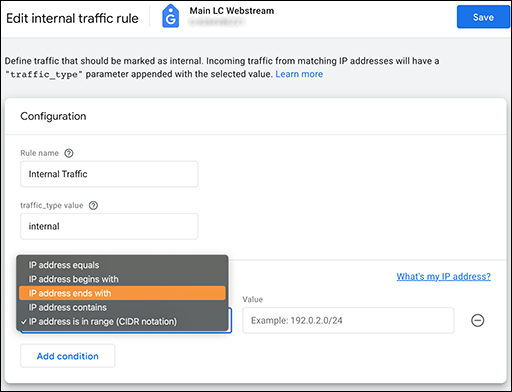 Internal Traffic Definition Dialog
Internal Traffic Definition Dialog
To filter internal traffic, you must define internal traffic, and then exclude that traffic. Define internal traffic by navigating to your data stream and selecting Configure tag settings > Define internal traffic, and enter your IP address configuration. Create the filter by navigating to Data Settings > Data Filters, and select Internal traffic exclude.
Filtering app developer traffic
App developer traffic is identified by different parameters, debug_mode or debug_event set to 1. The filtered traffic remains visible in DebugView, so developers can still verify their work.
Validate Exclusions and Internal Filters
Filters can be in Testing, Active, or Inactive mode. While in testing mode, traffic is evaluated, and the matching traffic is identified with a filter-specific dimension name. To test any filter, add the comparably named dimension filter to your traffic report to verify filter definition results.
Event-specific elements can be viewed in DebugView whether captured by Google tag, Google Tag Manager (GTM), or GA for Firebase.
RESOURCES
Data Filters: GA support covers filter types, modes, and steps to create, test, and activate.
DebugView: GA support provides event monitoring steps specific to Google tag, Google Tag Manager (GTM), and GA for Firebase implementations.
Exclude referrals: GA support explains how the ignore_referrer parameter is used, at both the property level and for individual events.
Filter internal traffic: GA support provides steps for defining internal traffic and creating an exclusion filter.
Identify unwanted referrals: Select the User Acquisition report, then customize by adding a dimension (e.g., page_referrer).
Referral Traffic Guide: Data Driven U’s article on referral traffic includes methods to find and identify unwanted referral traffic, steps to exclude, and how to manage and use referral traffic.
SERVICES
GA4 MIGRATION STEPS
STEP 1: IMPLEMENTATION PLANNING
Assess Your UA Configuration and Create Your GA4 Measurement Plan
STEP 2: PROPERTY
Create Property and Plan Tagging
STEP 3: TAGGING AND TRACKING
Connect Data Streams and Add GA4 Tags to Enable Data Collection
STEP 4: EXCLUSIONS AND FILTERS
Implement Exclusions and Filters to Maintain Clean User Data
STEP 5: GOALS MIGRATION
Map and Recreate UA Goals as GA4 Conversion Events
STEP 6: EVENTS
Map and Recreate Priority UA Events as GA4 Events
7: CONTENT GROUPING
Implement Content Groups with Tag Parameters and Variables
STEP 8: CUSTOM DIMENSIONS AND METRICS
Map and Recreate UA Dimensions and Metrics to GA4
STEP 9: AUDIENCES
Recreate UA Audiences by Configuring GA4 Conditions
STEP 10: LINKS AND INTEGRATIONS
Replicate Current Links and Integrations in GA4
STEP 11: REPORTS
Map Reporting Needs to Standard, Custom, and Exploration Reports
STEP 12: VALIDATE, PREP, LAUNCH
Validate GA4 Data, UA Archival, and User Readiness and Launch
Need help with your GA4 migration?
Businesses depend on accurate, relevant data in a tuned analytics platform. With the UA sunset approaching, create a migration plan that matches your need and expands capabilities. We can help you get there.




